Algorithms
Analysis of algorithms
Approximation algorithm
Computability theory
Evolutionary algorithm
Genetic algorithm
Numerical analysis
Online algorithm
Quantum algorithm
Randomized algorithm
Sorting algorithm
Algorithmic graph theory and combination
Computational geometry
Computing technology and Application
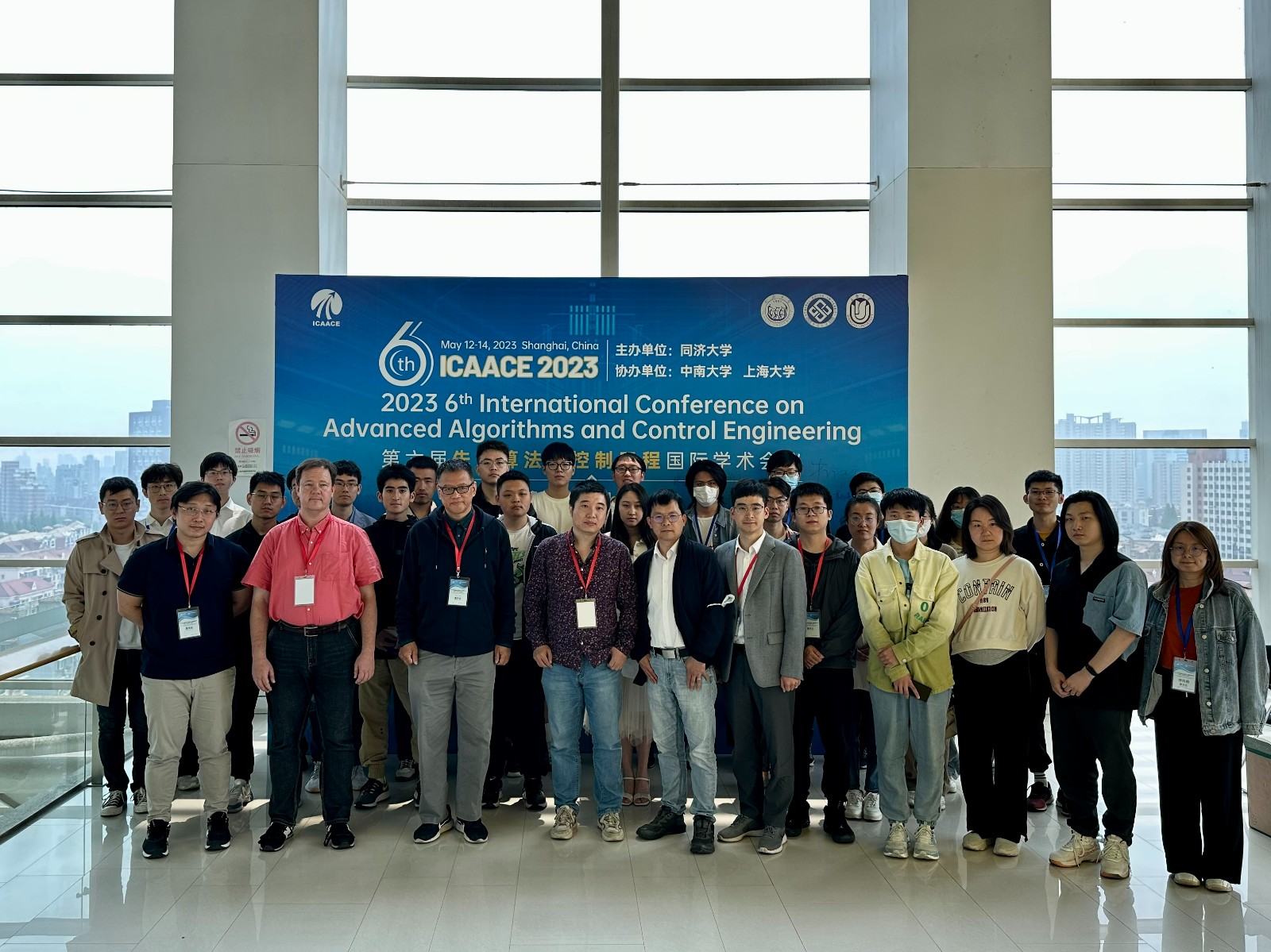






 Please send the full paper(word+pdf) to Submission System :
Please send the full paper(word+pdf) to Submission System : 
 All papers, both invited and contributed, the accepted papers, will be published and submitted for inclusion into IEEE Xplore subject to meeting IEEE Xplore’s scope and quality requirements, and also submitted to EI Compendex and Scopus for indexing. All conference proceedings paper can not be less than 4 pages.
All papers, both invited and contributed, the accepted papers, will be published and submitted for inclusion into IEEE Xplore subject to meeting IEEE Xplore’s scope and quality requirements, and also submitted to EI Compendex and Scopus for indexing. All conference proceedings paper can not be less than 4 pages.
